Mapping NVIDIA's Full GenAI Toolchain

# Generative AI
# AI Frameworks
# NVIDIA
Part 1: A Practitioner’s Guide to NVIDIA’s GenAI Stack
December 10, 2025
Kopal Garg

Generative AI systems need more than powerful models; they depend on the software and infrastructure that can train, serve, and scale them efficiently. NVIDIA’s AI Enterprise Software Reference Architecture organizes its tools into layers that cover the full lifecycle: building, optimizing, deploying, and managing AI at scale.
I pulled together the diagram below to make sense of NVIDIA’s AI Enterprise Software Reference Architecture. This guide shows how these can be applied in practical GenAI workflows, along with examples and non-NVIDIA equivalents.
Here’s my breakdown, with GenAI use cases for each tool.
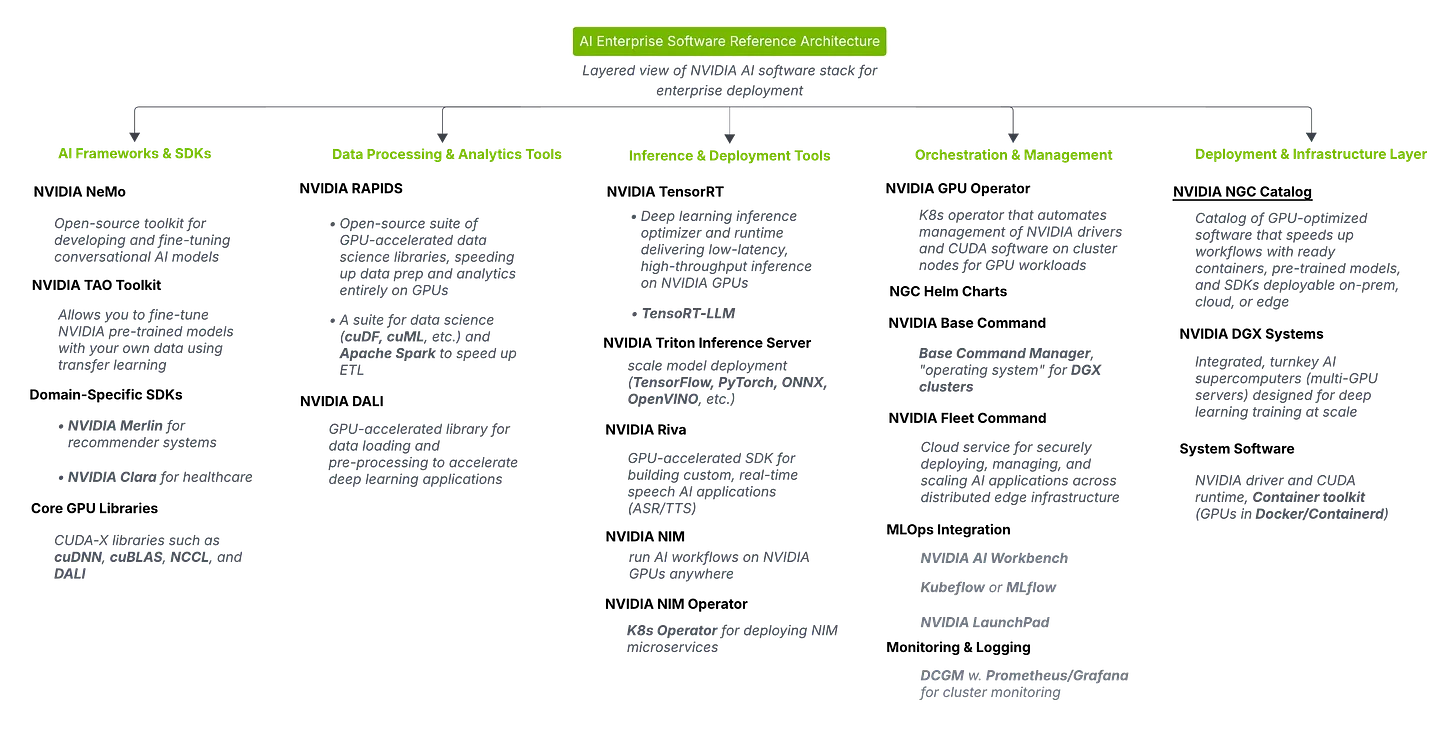
AI Frameworks & SDKs:
Where you build and fine-tune the brains of your system
NVIDIA NeMo
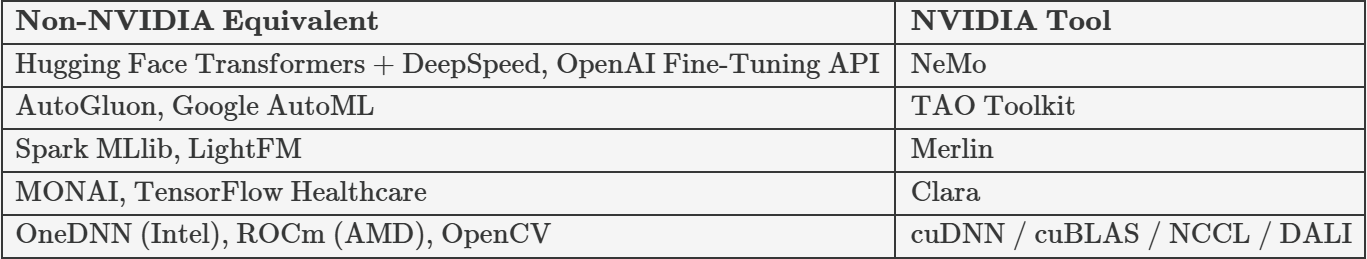
What is it? An open-source framework for training and fine-tuning large language models, ASR, TTS, and multimodal models. It has ready-to-use pipelines for pretraining and fine-tuning, plus domain adaptation tools so you can customize vocabularies and tokenizers. Built to handle massive models with Megatron-LM integration.
Example: Fine-tune a legal Q&A model so it understands Latin legal terms and cites case law accurately.
Integration tip: Pair with FAISS-GPU or Milvus for RAG, and deploy through Triton for production.
NVIDIA TAO Toolkit
What is it? Transfer learning without building training loops from scratch. You can adapt vision, speech, and NLP models in a low-code way.
Example: Fine-tune a speech-to-text model on your call center data in a few hours without writing custom training loops.
Domain-Specific SDKs
What is it? Pre-optimized kits for specialized industries. These are industry-optimized kits to shortcut development.
Examples:
Merlin → Build personalized product recommenders in an e-commerce chatbot (like “users who read this also liked…”).
Clara → Use healthcare-specific AI in a patient-facing Q&A assistant.
Core GPU Libraries
What is it? The CUDA-X building blocks that make everything faster. They speed up deep learning math, data loading, and GPU-to-GPU communication.
Examples: NCCL lets multiple GPUs “talk” super fast so a big LLM can run across them without slowdown.
Data Processing & Analytics Tools:
Where you clean, prep, and transform raw data into AI-ready formats - at GPU speed

RAPIDS (cuDF, cuML, cuGraph, etc.)
What is it? Think Pandas or Spark, but everything stays in GPU memory. This removes the CPU as a bottleneck.
Example: Process millions of PDFs, clean the text, and generate embeddings in hours instead of days.
NVIDIA DALI
What is it? Loads and preprocesses data directly on the GPU so your model is never idle waiting for the next batch.
Example: Normalize and batch massive image datasets for a multimodal RAG pipeline, removing the I/O bottleneck.
Integration tip: NCCL uses NVLink/InfiniBand for multi-GPU all-reduce; DALI keeps preprocessing in GPU memory.
Inference & Deployment Tools:
Where you turn trained models into fast, reliable services.
NVIDIA TensorRT
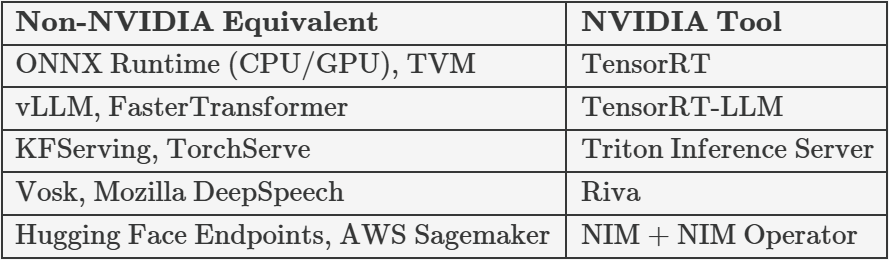
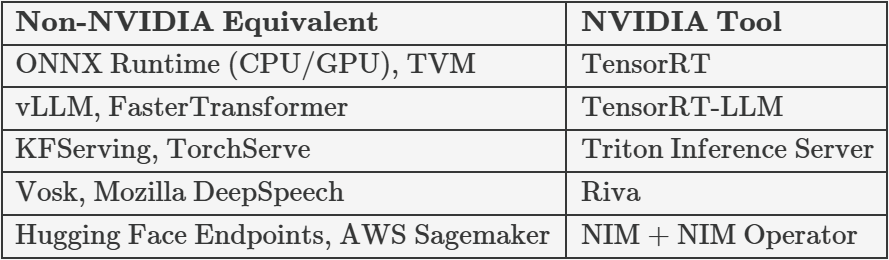
What is it? Optimizes models for much faster inference through kernel fusion and mixed precision.
Example: Cut chatbot latency from 1 second to 0.5 seconds without losing accuracy.
Integration tip: Use before deployment to Triton for max throughput.
TensorRT-LLM
What is it? Optimized for large language models with paged KV cache and speculative decoding.
Example: Serve a 70B model at high QPS for customer support without doubling GPU count.
NVIDIA Triton Inference Server
What is it? One API for serving models from TensorFlow, PyTorch, ONNX, OpenVINO, and more. Auto-batches requests to get the most from your GPUs.
Example: Host your embedding model and reranker together and let Triton batch requests automatically.
NVIDIA Riva
What is it? A real-time speech AI SDK for streaming ASR and TTS.
Example: Add a voice interface to your RAG assistant so it can take spoken queries and respond aloud instantly.
Technical integration: Pair with Triton or NIM for unified deployment.
NVIDIA NIM + NIM Operator
What is it? Prepackaged AI microservices you can deploy on any GPU environment in minutes.
Example: Deploy a retrieval API for your RAG app without touching CUDA installs.
Orchestration & Management:
Where you keep all the moving parts running - and scaling - in production.
NVIDIA GPU Operator
What is it? Handles GPU driver and CUDA setup in Kubernetes automatically.
Example: Add a new GPU node to your inference cluster and have it production-ready in minutes.
NVIDIA Base Command
What is it? The control center for DGX systems.
Example: Monitor a multi-node LLM training job and restart failed tasks automatically.
NVIDIA Fleet Command
What is it? Securely deploy and update AI apps across distributed sites.
Example: Push a new model version to hundreds of retail store edge nodes overnight.
MLOps Integrations (AI Workbench, Kubeflow, MLflow)
What is it? Tools for tracking experiments, automating pipelines, and managing model versions.
Example: Swap in a new reranker model and roll back instantly if something breaks.
Monitoring & Logging (DCGM + Prometheus/Grafana)
What is it? Full GPU fleet observability.
Example: Catch GPUs running hot before they throttle and slow down your responses.
Deployment & Infrastructure Layer:
Where your workloads actually run.
NVIDIA NGC Catalog
What is it? A marketplace of GPU-optimized containers, models, and SDKs.
Example: Start a multimodal RAG proof-of-concept in hours by pulling a prebuilt NeMo container.
NVIDIA DGX Systems
What is it? GPU supercomputers with NVLink for large-scale AI training.
Example: Train a domain-specific 70B LLM in days instead of weeks.
System Software (CUDA toolkit, container runtime)
What is it? The foundation for running any GPU workload in Docker or Kubernetes.
Example: Deploy your entire RAG pipeline in containers with full GPU acceleration.
The examples here are starting points. In practice, you’ll mix and match based on your model type, data sources, latency requirements, and operational constraints. The key is to treat this stack as a set of interchangeable building blocks rather than a rigid recipe, that’s how you’ll get from a promising prototype to a production system that lasts.

Deployment & Infrastructure Layer: Hardware
Where your workloads physically live, with the raw compute, memory, and networking to make large-scale AI possible.
NVIDIA H100 / A100 / L4

What is it? Data center GPUs for AI training and inference.
Why it’s useful:H100: Transformer Engine for mixed precision, ideal for large LLMs.A100: Excellent for both training and inference, widely deployed.L4: Optimized for energy-efficient inference and media processingExample: Train and serve a multi-billion parameter LLM with low latency.
NVIDIA DGX Systems

What is it? Turnkey AI supercomputers with NVLink/NVSwitch interconnects for multi-GPU scaling.
Why it’s useful:NVLink/NVSwitch enables multi-node model parallelism without network bottlenecksExample: Run multi-node model parallel training for a 70B parameter chatbot.
HGX & MGX Platforms
What is it? Modular reference architectures for OEM partners.
Example: OEM builds an HGX H100 8-GPU server with liquid cooling for dense video analytics
Grace CPU & Grace Hopper


What is it?
Grace CPU: ARM-based CPU optimized for AI and HPC workloads.
Grace Hopper: Superchip combining Grace CPU + Hopper GPU with high-bandwidth NVLink-C2C.
Why it’s useful:Massive memory bandwidth, ideal for retrieval-augmented LLMs and large graph neural networks.Reduces latency in CPU–GPU data transfers.Example: Optimize large memory-bound inference without bottlenecks.
NVIDIA Jetson Platform


What is it? Edge AI devices for robotics, IoT, and embedded AI.
Why it’s useful:Runs CUDA and TensorRT on small, low-power devices.Great for latency-sensitive inference without relying on cloud connectivity.Example: Deploy an on-device LLM-powered voice assistant in a drone.
NVIDIA’s hardware portfolio spans from large-scale AI supercomputers to compact edge devices, each designed with specific computational resources to target different AI deployment needs.
